Menstrual Cycle: Phases, Symptoms, and Tips for a Healthy Cycle
The menstrual cycle is a natural process in a woman’s body that prepares for pregnancy each month. It involves hormonal changes that regulate ovulation and menstruation. Understanding the cycle helps in maintaining reproductive health, identifying irregularities, and managing period-related discomfort.
What is the Menstrual Cycle?
The menstrual cycle is a monthly hormonal cycle that a woman’s body goes through to prepare for a possible pregnancy. It typically lasts 28 days but can range between 21 to 35 days in different individuals. The cycle begins on the first day of menstruation (period) and ends when the next period starts.
Phases of the Menstrual Cycle
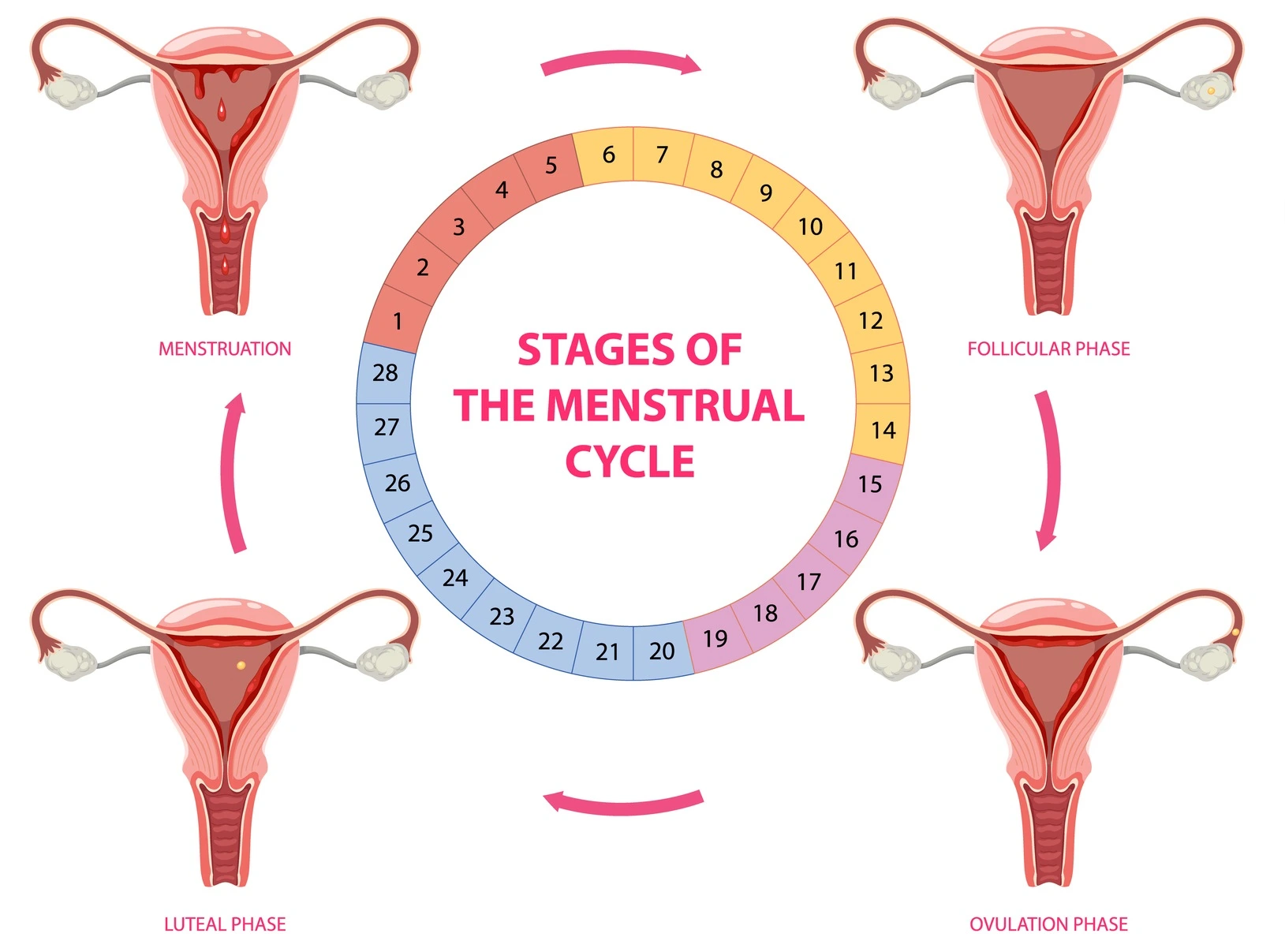
The menstrual cycle is divided into four phases, each with different hormonal changes and effects on the body.
1. Menstrual Phase (Days 1–5)
- This phase starts when the uterine lining (endometrium) sheds, resulting in menstrual bleeding.
- Common symptoms: Cramps, bloating, fatigue, lower back pain, mood swings.
- The hormone levels of estrogen and progesterone drop, signaling the body to start a new cycle.
2. Follicular Phase (Days 6–14)
- The pituitary gland releases follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), which stimulates the growth of eggs in the ovaries.
- The uterine lining starts thickening again to prepare for a possible pregnancy.
- Estrogen levels increase, improving mood and energy levels.
- Near the end of this phase, a dominant follicle matures, leading to ovulation.
3. Ovulation Phase (Day 14 – Middle of the Cycle)
- A surge in luteinizing hormone (LH) triggers the release of a mature egg from the ovary.
- This is the most fertile period of the cycle, meaning there is a high chance of pregnancy if sperm is present.
- Some women experience mild cramping, increased libido, and changes in cervical mucus (clear and slippery).
4. Luteal Phase (Days 15–28)
- The empty follicle (corpus luteum) produces progesterone, maintaining the uterine lining for a possible pregnancy.
- If the egg is not fertilized, hormone levels drop, leading to the shedding of the uterine lining (next period).
- Symptoms of PMS (premenstrual syndrome) may occur: mood swings, cravings, breast tenderness, bloating, and fatigue.
Common Menstrual Cycle Issues
While most women have regular cycles, some may experience irregularities due to hormonal imbalances, stress, or medical conditions.
1. Irregular Periods
- Periods that come too early, too late, or vary in length.
- Causes: Hormonal imbalance, stress, PCOS, thyroid issues, excessive exercise.
2. Heavy Periods (Menorrhagia)
- Excessive bleeding that lasts longer than 7 days.
- Causes: Fibroids, hormonal imbalance, endometriosis.
3. Painful Cramps (Dysmenorrhea)
- Severe cramps that interfere with daily life.
- Causes: Endometriosis, fibroids, or high prostaglandin levels.
4. Missed or Absent Periods (Amenorrhea)
- Missing periods for 3+ months (excluding pregnancy).
- Causes: Extreme weight loss, stress, PCOS, thyroid problems.
How to Maintain a Healthy Menstrual Cycle?
1. Eat a Balanced Diet
- Consume iron-rich foods (spinach, lentils, nuts) to prevent anemia.
- Include healthy fats (avocados, nuts) to balance hormones.
- Stay hydrated and limit processed foods and excessive caffeine.
2. Exercise Regularly
- Engage in moderate exercises like yoga, walking, or strength training to reduce PMS symptoms.
- Avoid over-exercising, which can disrupt hormone levels.
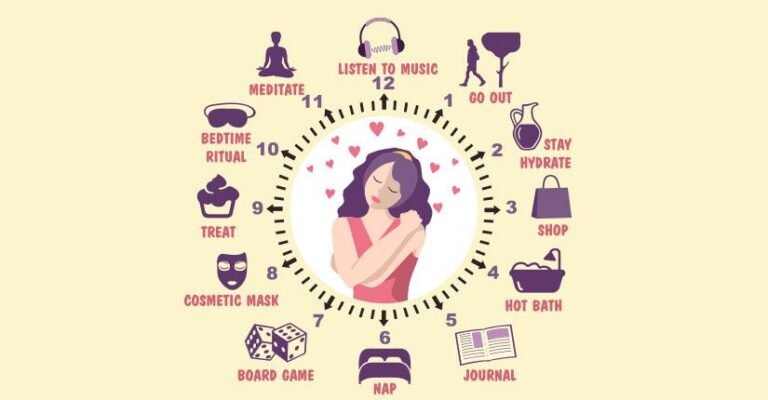
3. Manage Stress
- High stress can lead to irregular cycles. Practice meditation, deep breathing, or relaxation techniques.
4. Track Your Cycle
- Use period-tracking apps to monitor cycle length, symptoms, and ovulation days.
- Helps in identifying irregularities and planning for pregnancy.
5. Get Enough Sleep
- Poor sleep affects hormone production. Aim for 7–8 hours of sleep per night.
6. Consult a Doctor If Needed
- If you experience severe pain, very heavy bleeding, or irregular cycles, seek medical advice.
Final Thoughts
Understanding the menstrual cycle is essential for overall health. By maintaining a healthy diet, regular exercise, and stress management, women can ensure hormonal balance and prevent menstrual irregularities. If you notice unusual changes in your cycle, it’s best to consult a doctor for guidance.